Product Overview
Ranorex Studio
Automate even the most challenging desktop, web, or mobile app with Ranorex Studio's powerful test automation framework, including tools for codeless automation, a full IDE, and powerful API.
Specifications
Codeless Automation
Drag the slider bar to the right to see how easily beginners can build sophisticated tests with our codeless automation tools. Use powerful capture-and-replay functionality to record test actions. Add field validations and capture screenshots while recording. Drag-and-drop GUI elements or user code modules from the team’s shared repository into recorded actions. Easily build data-driven tests by adding links to data tables, spreadsheets or databases. Point-and-click to add parameters or conditions to test cases.
Achieve test automation goals
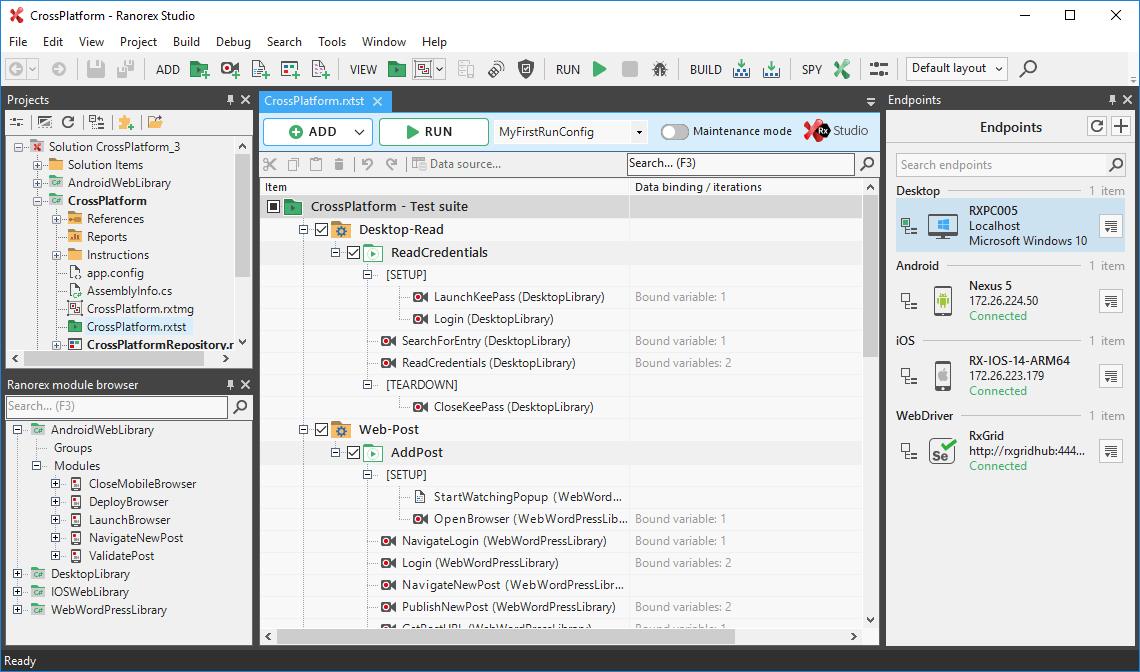
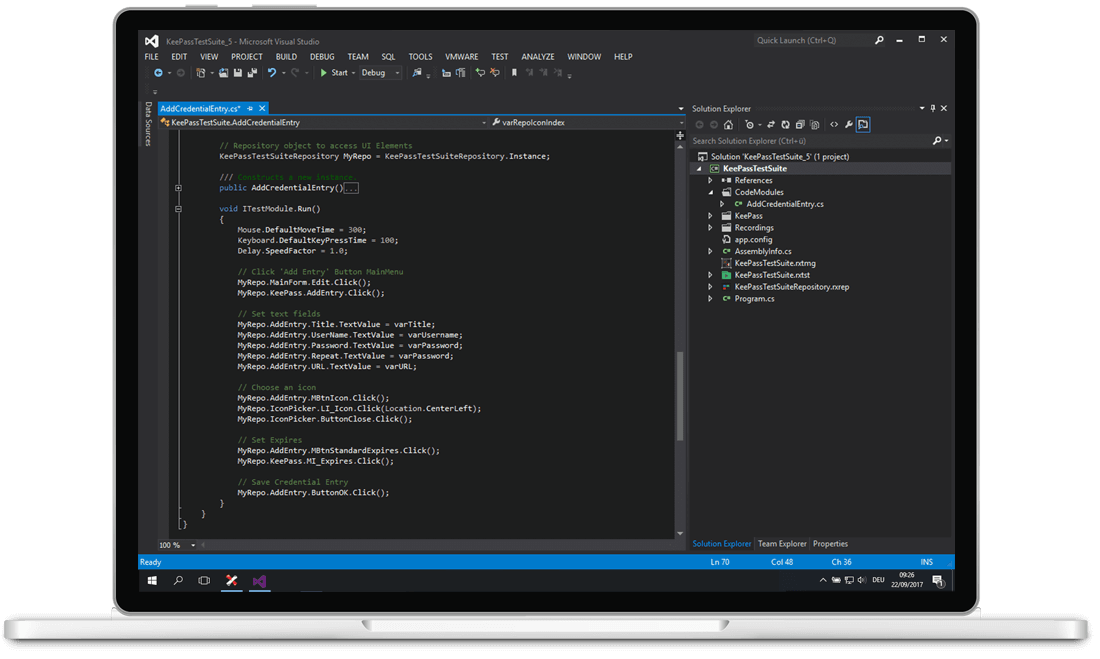
Full IDE
Drag the slider bar to the left to see Ranorex Studio’s integrated development environment for testers who prefer to build automation modules using standard programming languages. Our full IDE for C# and VB.NET includes productivity features such as intelligent code completion, tools for debugging and refactoring, automation helpers, and more. Boost team productivity by creating and sharing automation modules as user code collections and methods. Collaborate effectively with support for source control and the Ranorex Magic Merger tool.
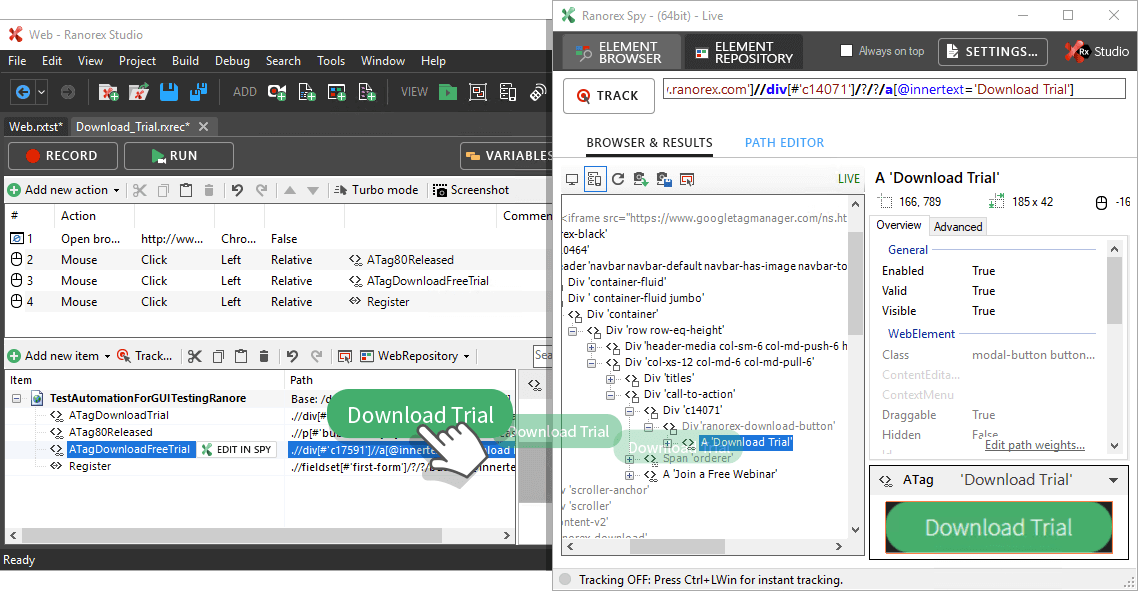
Strong UI element identification
Locate UI elements without knowledge of the underlying architecture.
Icon data-driven testing
Data-driven and keyword-driven testing
Easy-to-use tools empower testers to build sophisticated tests without coding
Icon collaboration
Collaborate with everyone on the team
Increase efficiency with a shareable object repository and user code library.
Integrate with your toolchain
Ranorex fits in your toolchain, from BDD specifications to CI server and defect tracking.
Black box testing vs white box testing
Combine black box, gray box and white box testing for the most comprehensive analysis of your application.
Black box tests are developed from sources such as user stories and functional specifications. They enable QA to focus on verifying features and usability without reliance on the underlying code. This can help catch defects that might be missed due to assumptions about the code.
By contrast, white box tests such as unit and integration tests are created with an understanding of the internals of the application and access to the source code. White box testing may catch defects that are unobserved or that can’t be tested directly in the user interface. Gray box tests combine the other approaches: they are developed from the user perspective, but with some understanding of how particular features were implemented.
A combination of black box, grey box and white box testing allows you to benefit from the strengths of each approach and offset the drawbacks.
Blackbox testing approaches
What are black box testing techniques?
In black box testing, functional test cases are developed through analysis of the available documentation, including requirements, specifications, user stories or scenarios. The black box approach can also be used for non-functional tests, such as security and performance tests. Some common black box testing approaches are described below:
Edge cases
Edge cases validate the minimum and maximum acceptable value of a single field, such as for a date or the length of a password. So if a field should allow entries in the range from 1 to 100, create one test case for the value of 1, and another for the value of 100. It is not necessary to test all of the values in between.
Corner cases
Corner cases test combinations of edge cases. The idea here is that while the individual fields may work properly, the combination may not. For example, if your application accepts a start date and an end date, a corner case would check a combination such as the earliest possible start date with the earliest possible end date.
Boundary cases
Boundary cases test values just outside and inside of the edge cases. To test value that is valid between 1 and 100, create edge cases for 0, 1 and 2; plus 99, 100 and 101. If the application handles the boundary values properly, then all other values should be handled correctly as well. This technique is also referred to as “boundary value analysis.”
User scenario cases
Scenarios describe the goal that a user wants to accomplish, such as checking their account balance or changing their password. In behavior-driven development (BDD), scenarios follow a specific “Given-When-Then” syntax that facilitates the creation of test cases.
Decision table testing
In this formal testing technique, the causes/inputs and effects/outputs in the application are arranged in a table, with each cell containing a unique cause/effect combination. Then a test case is created for each cell value.
Icon error guessing technique
Error guessing
In error guessing, testers use their knowledge of the system and experience to guess the types of defects that may exist, and build test cases for them. This technique is similar to exploratory testing, as both rely heavily on the skill and knowledge of the tester.
Increase visibility
Integrated automated testing increases visibility and allows teams to detect software defects faster, and assess the impact of software changes on business goals.
Faster releases
Release high quality software faster
The accelerated feedback loop ultimately leads to more stable builds and enables your team to release reliable, high-quality software faster.
Videos
Morgan Stanley
Reviewed on Sept. 3, 2024Ranorex Studio is a powerful and versatile test automation tool that simplifies the testing process with its user-friendly interface and comprehensive features.